Notes Payable Definition, Journal Entries, and Examples

At the end of the month, the journal entry is debiting interest expense $ 500 and credit interest payable $ 500. The interest can be compounded, meaning that interest is added to the principal amount of the loan and then the interest is charged on the new balance. Interest payable is often recorded on a quarterly or annual basis, comprehensive income depending on the terms of the loan agreement. At the end of the first month, as the company accrues $20,000 in interest, the company would debit $20,000 as interest expense and credit the same amount as the interest payable balance sheet. The journal entry is used to record the amount of interest paid to the creditors.
Organization
Regardless of when the bonds are physically issued, interest starts to accrue from the most recent interest date. Firms report bonds to be selling at a stated price “plus accrued interest”. The issuer must pay holders of the bonds a full six months’ interest at each interest date. Thus, investors purchasing bonds after the bonds begin to accrue interest must pay the seller for the unearned interest accrued since the preceding interest date. The bondholders are reimbursed for this accrued interest when they receive their first six months’ interest check. Each year Valley would make similar entries for the semiannual payments and the year-end accrued interest.
Interest Payment: Issued at a Discount
Since it’s a liability, interest payable accounts are recorded on the balance sheet and are due by the end of the accounting year or operating cycle. Wages Payable is a liability account that reports the amounts owed to employees as of the balance sheet date. Amounts are routinely entered into this account when the company’s payroll records are processed. A review of the details confirms that this account’s balance of $1,200 is accurate as far as the payrolls that have been processed. Up until that time, the future liability may be noted in the disclosures that accompany the financial statements. The interest expense is calculated by taking the Carrying Value($93,226) multiplied by the market interest rate (7%).
Journal Entry to Record Equipment Purchased and Issuance of Notes Payable
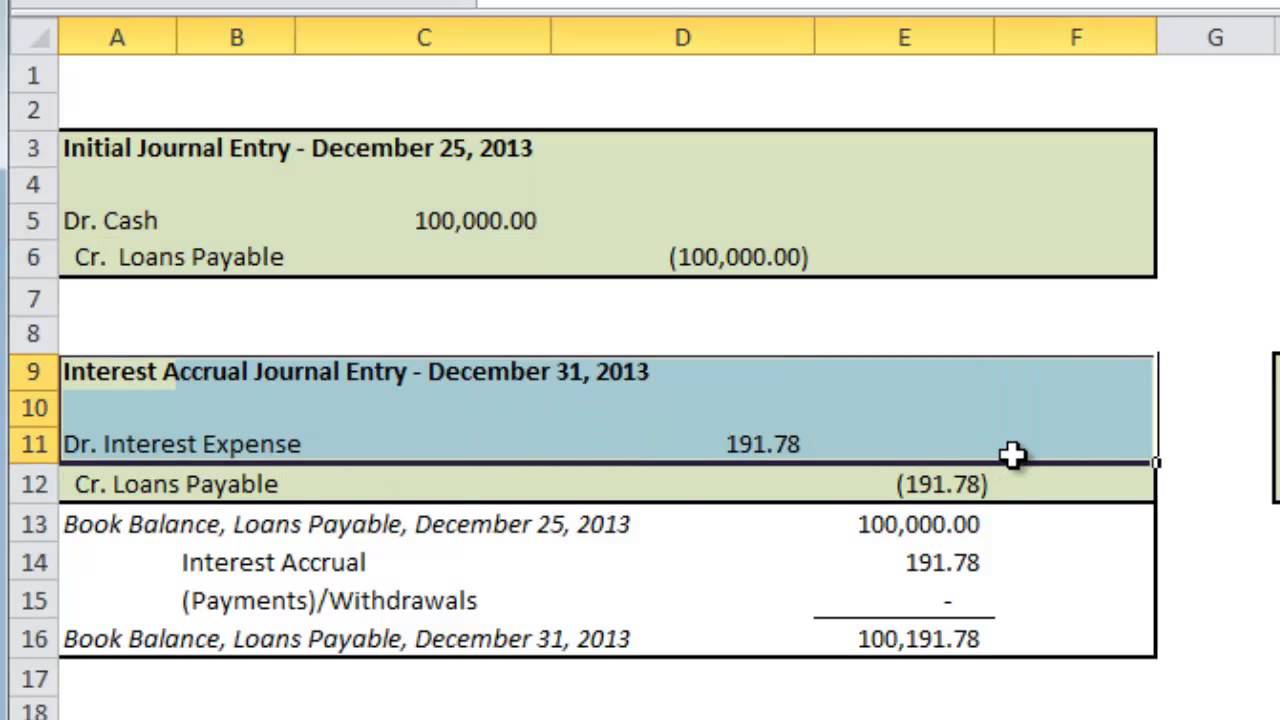
- On the December 31 balance sheet the company must report that it owes $25 as of December 31 for interest.
- At Finance Strategists, we partner with financial experts to ensure the accuracy of our financial content.
- Under the effective-interest method, the interestexpense is calculated by taking the Carrying (or Book) Value($104,460) multiplied by the market interest rate (4%).
- It is the amount of interest that a company owes to its creditors for a period of time.
- Now, since the loan was taken on 1st August 2017, the interest expense that would come in the income statement of the year 2017 would be for five months.
When you accrue interest as a lender or borrower, you create a journal entry to reflect the interest amount that accrued during an accounting period. On account of capital rents, an organization may need to deduce the measure of payable interest expense, in view of a deconstruction of the fundamental capital rent. Interest payable can incorporate costs that have already been charged or the costs that are accrued. The general ledger account for Notes Payable has been reduced by the amount of the principal portion of the payment, and should agree with the amortization schedule. Get up and running with free payroll setup, and enjoy free expert support. The creditors charge interest to the company base on the interest rate and accounting period.
Interest payable and interest expense are terms that are most often confused in their usage. Though they are meant for serving almost same objectives, there are differences that must be known to firms and individuals using them. And whenever expense increases for the company, the company debits the interest expense account and vice versa.
Which of these is most important for your financial advisor to have?
Thesebonds are issued in order to finance specific projects (such aswater treatment plants and school building construction) thatrequire a large investment of cash. The primary benefit to theissuing entity (i.e., the town or school district) is that cash canbe obtained more quickly than, for example, collecting taxes andfees over a long period of time. This allows the project to becompleted sooner, which is a benefit to the community. First, we will explore the case when the stated interest rate isequal to the market interest rate when the bonds are issued.
The customer record interest expense base on this period as well, it will not be related to the payment. At the time of payment, the company will debit the payable interest account because, after payment, the liability will be nil. When a company pays out cash, cash decreases, that’s why cash is being credited here.
Interest Expense is debited and Interest Payable is credited for three months of accrued interest. In order to calculate the amount of interest and principalreduction for each payment, banks and borrowers often useamortization tables. While amortization tables are easily createdin Microsoft Excel or other spreadsheet applications, there aremany websites that have easy-to-use amortization tables. Interest expenses are debits because in double-entry bookkeeping debits increase expenses.
The following example will explain interest payable more properly; a business owes $3,000,000 to a bank at a 5% financing cost and pays interest to the provider each quarter. The balance sheet or journal entry for interest payable enables firms to check and track their financial obligations and be prepared to bear them as and when scheduled. Based on these pieces of information, the financial statements are created. The interest expenses yet to be paid off by the time the balance sheet is prepared are recorded by the firm. Anything beyond that is discarded and left to be recorded in the next fiscal year.
If the entities want to know how much they would require paying for specific number of months, they can divide the annual interest figure by 12. This includes considering the notes payable, which is the amount that an individual or entity plans to borrow. This allows the businesses to be more accurate while calculating the interest expense for the period. Interest payable on balance sheet tells firms and keeps them alarmed about the financial obligations they have to fulfill. If any interest incurs after the date at which the interest payable is recorded on the balance sheet, that interest wouldn’t be considered. Sometimes corporations prepare bonds on one date but delay their issue until a later date.



